According to the official ISO Survey 2023 results showing 48,671 valid ISO 27001 certificates worldwide, organizations typically invest $25,000 to $250,000 and 6-18 months pursuing ISO 27001 certification. However, research from leading cybersecurity consultancies indicates that approximately 40% of organizations fail their initial certification audit due to inadequate preparation, unrealistic timeline expectations, and insufficient resource allocation.
This comprehensive guide eliminates the guesswork by providing evidence-based cost breakdowns, realistic timelines, and a proven step-by-step process derived from analysis of successful certification projects across multiple industries and organization sizes. Whether you’re a CISO planning your first certification or a business leader evaluating the investment, you’ll discover exactly what ISO 27001 certification requires, how much it truly costs by company size, and how to choose the right certification body.
For detailed analysis of specific aspects covered in this guide, explore our comprehensive resources: ISO 27001 Certification Cost: 2025 Budget Breakdown by Company Size for complete financial planning, ISO 27001 Certification Timeline: Realistic Planning Guide for 2025 for detailed project scheduling, and ISO 27001 Multi-Site Certification: When It Saves Money vs When It Costs More (2025 Analysis) for organizations with multiple locations. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about ISO 27001 certification success in 2025.
What is ISO 27001 Certification? (Complete Definition for 2025)
ISO 27001 certification validates that your organization’s Information Security Management System (ISMS) meets international standards for protecting sensitive data through systematic risk management and security controls.
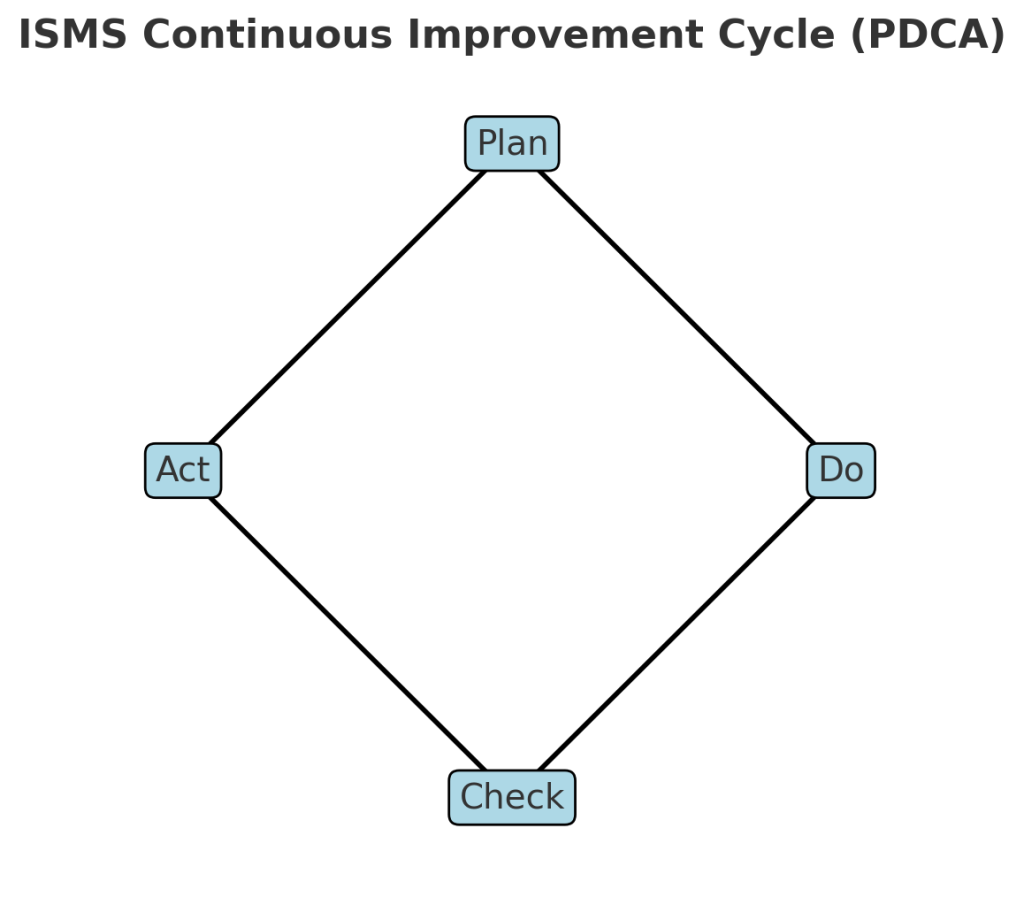
Think of ISO 27001 certification as a comprehensive security audit report card that demonstrates to customers, partners, and regulators that your organization takes information security seriously. Unlike basic security assessments, ISO 27001 certification requires ongoing commitment to continuous improvement and regular surveillance audits.
Certification vs. Compliance: Understanding the Difference
Many organizations confuse ISO 27001 compliance with certification. Compliance simply means following the standard’s requirements internally, while certification involves an independent third-party audit that validates your implementation. Certification provides external credibility that compliance alone cannot offer.
Individual vs. Organizational Certification
ISO 27001 offers two certification paths:
- Organizational Certification: Your company receives an ISO 27001 certificate validating its ISMS
- Individual Certification: Professionals can become certified ISO 27001 Lead Implementers, Lead Auditors, or Internal Auditors
This guide focuses on organizational certification, which is what most businesses pursue for competitive advantage and customer requirements.
2022 Standard Updates and 2025 Implications
The ISO 27001:2022 revision introduced several important changes:
- 11 new security controls addressing cloud security, data privacy, and threat intelligence
- Greater emphasis on organizational context and stakeholder requirements.
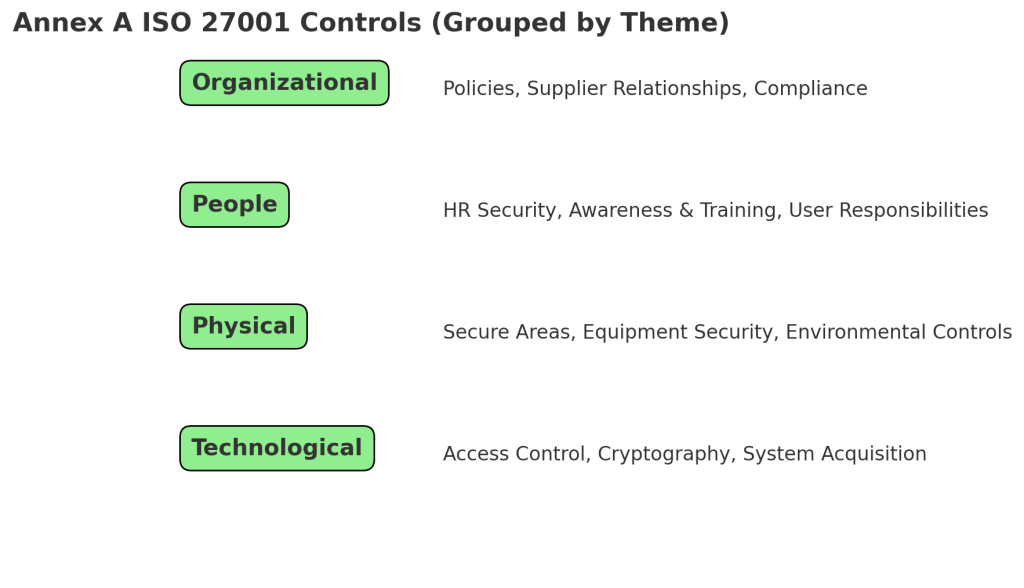
- Streamlined control that reduces the control categories from 14 down to 4 main themes.
- Improved alignment with other management system standards
These updates also impacted Annex A, where the 93 controls were reorganized into the new four-theme model. This grouping makes it easier for organizations to understand how controls fit together and supports a more practical approach to implementation.
Organizations certified under the 2013 version had until October 2025 to transition, making 2025 a critical year for many certification projects.
Global Recognition and Industry Acceptance
ISO 27001 is recognized in over 160 countries and is often mandatory for:
- Government contractor relationships
- Financial services partnerships
- Healthcare data processing agreements
- Cloud service provider certifications
- International business expansion
Why Get ISO 27001 Certified? (ROI & Business Impact Analysis)
The business case for ISO 27001 certification extends far beyond compliance checkboxes. Organizations report measurable returns on investment within 18 months of certification, with benefits spanning customer acquisition, risk reduction, and operational efficiency.
Measurable ROI and Financial Benefits
Industry research demonstrates compelling financial returns:
- Average ROI: 300% within 18 months of certification
- Revenue impact: Certified companies win 40% more enterprise deals
- Risk reduction: 60% average reduction in security incidents post-certification
- Insurance benefits: 20-30% potential reduction in cyber insurance premiums
- Operational efficiency: 25% improvement in incident response times
Customer Trust and Market Access
In today’s security-conscious business environment, ISO 27001 certification has become a competitive differentiator:
- 85% of enterprise buyers require security certifications from vendors
- Government contracts increasingly mandate ISO 27001 certification
- International expansion becomes easier with globally recognized credentials
- Partnership opportunities expand as certification demonstrates security maturity
Competitive Advantage in Sales Processes
Sales teams report significant advantages during enterprise sales cycles:
- Shortened sales cycles as security objections are eliminated early
- Higher win rates against non-certified competitors
- Premium pricing opportunities for security-validated services
- RFP qualification automatic inclusion in security-sensitive procurements
The combination of external market advantages and internal operational improvements typically justifies certification investments within the first year of achieving certification.
Who Needs ISO 27001 Certification? (2025 Requirements & Eligibility)
ISO 27001 certification requirements have evolved significantly, with 2025 marking a pivotal year for many organizations as transition deadlines approach and market expectations increase.
Company Size Requirements and Practical Considerations
No minimum company size exists for ISO 27001 certification, but practical considerations vary:
Small Companies (1-50 employees):
- Certification is achievable but requires dedicated resources
- Simplified ISMS scope often focuses on core business processes
- Typical certification timeline: 6-9 months
- Investment range: $25,000-$50,000
Medium Companies (51-250 employees):
- Most cost-effective certification segment
- Balanced resource availability and complexity
- Typical certification timeline: 9-12 months
- Investment range: $50,000-$100,000
Large Companies (250+ employees):
- Complex multi-site implementations common
- Dedicated compliance teams typically required
- Typical certification timeline: 12-18 months
- Investment range: $100,000-$250,000
Industry-Specific Certification Drivers
Certain industries face increased certification pressure:
Healthcare Organizations:
- HIPAA compliance requirements increasingly reference ISO 27001
- Patient data protection regulations demand systematic security approaches
- Healthcare IT vendors often require certification for partnerships
Financial Services:
- Regulatory expectations for robust security frameworks
- Customer due diligence requirements for third-party risk management
- Competitive differentiation in fintech and digital banking
Technology Companies:
- SaaS providers face customer certification requirements
- Cloud service providers need certification for enterprise sales
- Software companies handling customer data must demonstrate security controls
Timeline Triggers for Certification Planning
Specific business events often drive certification initiatives:
- IPO Preparation: Due diligence processes examine security frameworks
- Merger & Acquisition Activity: Security due diligence evaluates existing certifications
- Major Customer Negotiations: Enterprise sales cycles include security requirement discussions
ISO 27001 Certification Requirements (2025 Prerequisites Checklist)
Successful ISO 27001 certification requires systematic preparation across documentation, processes, technology, and organizational readiness. Understanding these prerequisites prevents costly delays and ensures efficient certification progress.
ISMS Foundation Elements
Before pursuing certification, organizations must establish core ISMS components:
Risk Assessment Framework:
- Formal risk identification methodology
- Asset inventory and classification system
- Threat and vulnerability assessment processes
- Risk treatment decision criteria and approval workflows
Security Policy Foundation:
- Information Security Policy approved by senior management
- Acceptable Use Policy defining employee responsibilities
- Access Control Policy governing system permissions
- Incident Response Policy outlining breach procedures
Documentation Requirements and Standards
ISO 27001 mandates specific documentation that auditors will examine:
Mandatory Documents (15 required):
- ISMS scope and boundaries definition
- Information Security Policy
- Risk assessment methodology and procedures
- Risk treatment plan and implementation timeline
- Statement of Applicability with control justifications
Supporting Documentation (30+ typical documents):
- Network architecture diagrams and data flow maps
- Asset registers and classification matrices
- Vendor management and third-party risk assessments
- Business continuity and disaster recovery plans
- Change management procedures and approval workflows
Organizational Readiness and Resource Allocation
Certification success requires committed organizational support:
Management Commitment Requirements:
- Executive sponsorship with allocated budget authority
- Appointed management representative for ISMS oversight
- Resource allocation for implementation and maintenance
- Policy approval authority and organizational communication
Timeline for Preparation and Implementation:
Months 1-2: Foundation and Planning
- Executive commitment and resource allocation
- ISMS scope definition and boundary establishment
- Project team formation and role assignment
- Initial gap analysis and readiness assessment
Months 3-6: Control Implementation and Documentation
- Security control deployment and configuration
- Procedure development and approval
- Training program delivery and record keeping
- Evidence collection and documentation organization
Step-by-Step ISO 27001 Certification Process (8-Step Roadmap)
The ISO 27001 certification process follows a systematic approach that ensures audit success and maintains ongoing compliance. This proven 8-step roadmap provides specific timelines and milestone markers.
Step 1: Project Planning and Scope Definition (Weeks 1-2)
Objective: Establish project foundation and define ISMS boundaries
Key Activities:
- Secure executive sponsorship and budget approval
- Appoint ISMS Manager and assemble cross-functional team
- Define ISMS scope including locations, processes, and systems
- Develop project charter with timeline, budget, and success criteria
Deliverables:
- ISMS Scope Statement with inclusion/exclusion rationale
- Project Charter with approved budget and timeline
- Team responsibility matrix and communication plan
Step 2: Risk Assessment and Gap Analysis (Weeks 3-6)
Objective: Understand current security posture and identify improvement requirements
Key Activities:
- Conduct comprehensive asset inventory and classification
- Perform threat and vulnerability assessment across all assets
- Execute risk analysis using quantitative or qualitative methodology
- Compare current controls against ISO 27001 Annex A requirements
Deliverables:
- Asset Register with classification and ownership assignment
- Risk Assessment Report with threat and vulnerability analysis
- Gap Analysis Report comparing current state to ISO 27001 requirements
Step 3: ISMS Design and Policy Development (Weeks 7-12)
Objective: Design ISMS architecture and develop required policies
Key Activities:
- Develop Information Security Policy and supporting procedures
- Create risk management methodology and implementation procedures
- Design control selection criteria and implementation guidelines
- Establish measurement and monitoring frameworks
Deliverables:
- Information Security Policy approved by senior management
- Risk Management Procedures with methodology and criteria
- Security Control Implementation Guidelines
Step 4: Control Implementation and Documentation (Weeks 13-20)
Objective: Deploy security controls and document implementation evidence
Key Activities:
- Implement technical controls including access management and network security
- Deploy administrative controls including policies and training programs
- Establish physical controls for facility and equipment protection
- Configure monitoring and logging systems for control effectiveness measurement
Deliverables:
- Technical Control Implementation with configuration documentation
- Administrative Control Deployment with training records
- Control Implementation Evidence organized by Statement of Applicability
Step 5: Employee Training and Awareness Programs (Weeks 18-22)
Objective: Ensure organizational competency and security awareness
Key Activities:
- Deliver security awareness training to all employees
- Provide role-specific training for positions with security responsibilities
- Train internal audit team on ISO 27001 requirements and audit procedures
- Conduct tabletop exercises for incident response and business continuity
Success Criteria:
- 100% employee completion of security awareness training
- Demonstrated competency for security-responsible roles
- Qualified internal audit team capable of ISMS assessment
Step 6: Internal Audit and Management Review (Weeks 23-26)
Objective: Validate ISMS effectiveness before external audit
Key Activities:
- Execute comprehensive internal audit covering all ISMS requirements
- Review control implementation effectiveness and evidence quality
- Identify nonconformities and develop corrective action plans
- Conduct management review of ISMS performance and effectiveness
Success Criteria:
- Internal audit demonstrates substantial ISMS compliance
- Nonconformities resolved with effective corrective actions
- Management review confirms ISMS suitability and effectiveness
Step 7: Certification Body Selection and Stage 1 Audit (Weeks 27-30)
Objective: Choose qualified certification body and complete documentation review
Key Activities:
- Evaluate certification body qualifications, experience, and accreditation
- Request proposals and compare pricing, timeline, and service offerings
- Submit audit application with ISMS documentation package
- Participate in Stage 1 audit focusing on documentation review
Success Criteria:
- Qualified certification body selected based on objective criteria
- Stage 1 audit confirms documentation adequacy and compliance
- Stage 1 findings resolved before Stage 2 audit scheduling
Step 8: Stage 2 Audit and Certificate Issuance (Weeks 31-34)
Objective: Complete certification audit and achieve ISO 27001 certificate
Key Activities:
- Participate in Stage 2 on-site audit with control testing and interviews
- Demonstrate control implementation effectiveness and operational maturity
- Address any audit findings with corrective action plans
- Receive ISO 27001 certificate and plan surveillance audit schedule
Success Criteria:
- Stage 2 audit demonstrates effective ISMS implementation
- ISO 27001 certificate issued without major findings
- Surveillance audit planning ensures ongoing compliance
Implementation Timeline Summary
Total Timeline: 34 weeks (8.5 months) for typical medium-sized organization
Critical Success Factors:
- Executive commitment maintained throughout implementation
- Adequate resource allocation for internal effort and external support
- Realistic timeline expectations with contingency planning
- Focus on control effectiveness rather than documentation volume
Certification Costs and Timeline Overview
For detailed cost breakdowns and budget planning, see our comprehensive guides:
- ISO 27001 Certification Costs: 2025 Budget Breakdown by Company Size – Complete analysis including hidden costs, ROI calculations, and cost reduction strategies
- ISO 27001 Certification Timeline: Realistic Planning Guide – Detailed timeline analysis, delay factors, and acceleration strategies
Quick Cost Reference
Small Companies (1-50 employees): $25,000-$50,000 total investment Medium Companies (51-250 employees): $50,000-$100,000 total investment
Large Companies (250+ employees): $100,000-$250,000 total investment
Quick Timeline Reference
Simple Organizations: 6-9 months Complex Organizations: 9-15 months Multi-Site Organizations: 12-18 months
Choosing the Right Certification Body
Selecting the appropriate certification body significantly impacts your audit experience, costs, and long-term compliance success.
Essential Accreditation Verification
Key Accreditation Bodies:
- ANAB (ANSI National Accreditation Board) – United States
- UKAS (United Kingdom Accreditation Service) – United Kingdom
- DAkkS (Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle) – Germany
- IAF (International Accreditation Forum) – Global recognition
Evaluation Criteria
Technical Competency (30% weight):
- Industry expertise and relevant experience
- Audit team qualifications and certifications
- Technical knowledge depth and specialization
Service Quality (25% weight):
- Audit approach and methodology effectiveness
- Communication quality and responsiveness
- Report quality and improvement recommendations
Cost Effectiveness (20% weight):
- Total cost of ownership analysis
- Pricing transparency and structure clarity
- Value for money assessment
Geographic Coverage (15% weight):
- Operational location coverage
- Multi-site coordination capabilities
- Local presence and support
Major Certification Bodies:
BSI (British Standards Institution):
- Best For: Large organizations, international operations, regulated industries
- Strengths: Global presence, extensive industry experience
SGS (Société Générale de Surveillance):
- Best For: Multi-site organizations, cost-conscious implementations
- Strengths: Worldwide coverage, competitive pricing
Common Certification Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from common certification failures prevents costly mistakes and ensures audit success.
Top 5 Critical Mistakes
1. Inadequate Risk Assessment Documentation (35% of failures)
- Prevention: Comprehensive methodology training, external validation, regular review cycles
2. Insufficient Employee Training Programs (40% of implementation failures)
- Prevention: Targeted training programs, competency assessments, ongoing reinforcement
3. Last-Minute Audit Preparation (45% of audit failures)
- Prevention: Early audit scheduling, systematic preparation checklists, practice sessions
4. Underestimating Time Requirements (50% of project failures)
- Prevention: Realistic project planning, adequate resource allocation, stakeholder commitment
5. Overly Broad ISMS Scope (40% of scope-related failures)
- Prevention: Business-focused scope definition, risk-based boundaries, phased implementation
Success Factors
Executive Leadership and Commitment:
- Sustained senior management support throughout implementation and maintenance
- Adequate resource allocation with realistic timeline expectations
- Regular communication and progress reporting to stakeholder groups
Professional Expertise and External Support:
- Qualified consultant engagement for complex implementations
- Internal auditor training and certification programs
- Industry-specific expertise for specialized requirements
Conclusion: Your Path to Certification Success
ISO 27001 certification represents a significant investment in your organization’s security posture and competitive positioning. The key to success lies in realistic planning, adequate resource allocation, and systematic execution.
Essential Success Factors
Realistic Expectations:
- Budget $25,000-$250,000 depending on organization size and complexity
- Plan 6-18 months for complete certification achievement
- Expect ongoing maintenance costs of $10,000-$50,000 annually
Strategic Planning:
- Secure executive sponsorship and sustained management commitment
- Assemble qualified implementation team with clear roles and responsibilities
- Define realistic ISMS scope aligned with business objectives and risk tolerance
Professional Execution:
- Follow systematic 8-step implementation process with milestone tracking
- Invest in comprehensive employee training and competency development
- Maintain focus on control effectiveness rather than documentation volume
Immediate Next Steps
Week 1-2: Foundation Assessment
- Complete our Certification Readiness Assessment to identify current gaps
- Secure executive sponsorship and initial budget approval
- Define preliminary ISMS scope aligned with business objectives
- Assemble cross-functional implementation team with clear roles
Week 3-4: Planning and Preparation
- Develop detailed project charter with timeline and resource allocation
- Conduct comprehensive gap analysis using our assessment framework
- Request proposals from 3-5 qualified certification bodies
- Establish project governance and communication structures
Long-Term Value Maximization
Business Integration:
- Align ISMS objectives with broader business strategy and risk management
- Integrate certification messaging into sales and marketing communications
- Leverage certification for customer trust building and partnership development
Continuous Improvement:
- Establish regular performance monitoring and measurement cycles
- Plan surveillance audit preparation as ongoing operational activity
- Invest in automation tools for evidence collection and compliance monitoring
The investment in ISO 27001 certification pays dividends through enhanced customer trust, competitive differentiation, risk reduction, and operational efficiency. By following this proven framework, your organization can achieve certification success while building lasting security management maturity.
Frequently Asked Questions about ISO 27001
How long does ISO 27001 certification take?
Certification usually takes between 3–6 months for small businesses and up to 12 months for larger organizations, depending on resources, scope, and readiness.
What are the costs of ISO 27001 compliance?
Costs vary widely, but most organizations spend $5,000–$40,000, which includes gap assessments, training, internal resources, and auditor fees.
Is ISO 27001 mandatory in Canada/US?
ISO 27001 is not legally required in Canada or the US. However, many companies pursue it because it is often a contractual or industry expectation, especially in finance, healthcare, and SaaS.